?A research group led by Professor Yasufumi Takahashi at Nano Life Science Institute (WPI-NanoLSI), Kanazawa University / Graduate School of Engineering Nagoya University, together with researchers that National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Osaka University, Nagoya City University and University of Tsukuba have discovered a two-dimensional material called a "superatomic layer" in which cubic molybdenum sulfide clusters (*1) (superatom(*2)) are bonded in a sheet-like formation, and clarified its structural characteristics, electronic structure, and catalytic activity.?
By directly observing a single layer (nanoribbon (*3)) confined in nanospace with a transmission electron microscope, we were able to visualize the atomic arrangement and successfully determine the structure. In addition, evaluation of the catalytic activity of a thin sample of the layered material synthesized on the substrate demonstrated that it exhibits high catalytic activity for hydrogen evolution reactions. The results of this research are expected to serve as a guideline for the design of materials for the development of highly efficient hydrogen evolution catalysts.
The results of this research were published in the online preliminary edition of the German scientific journal Advanced Materials on July 26, 2024.
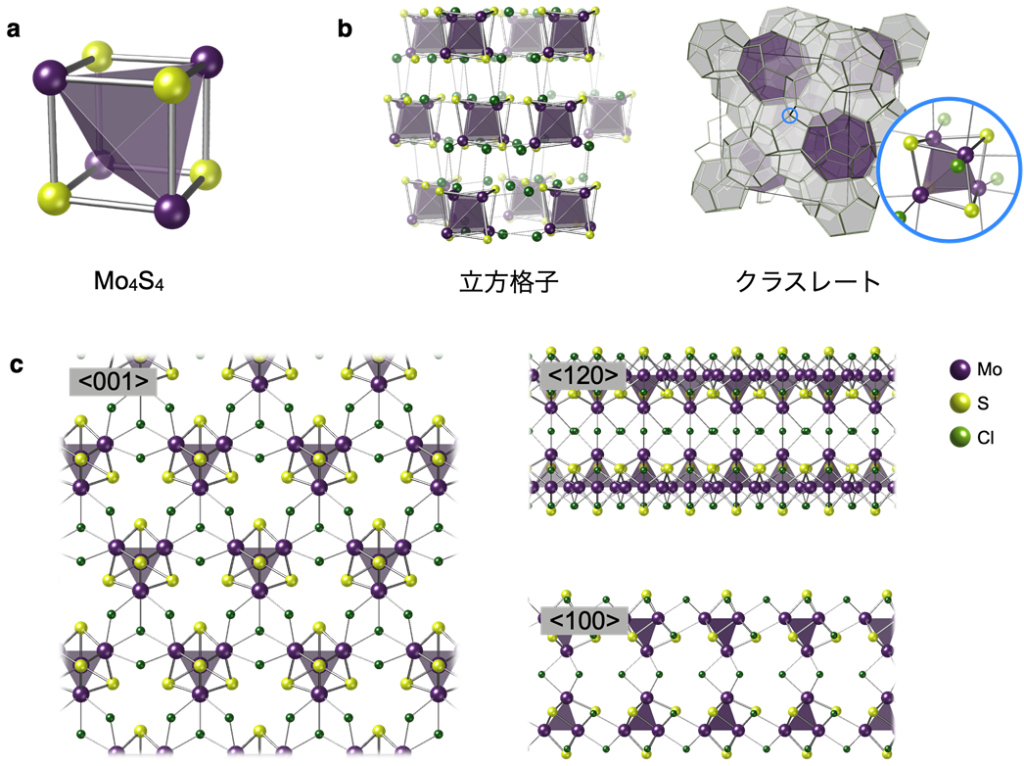 Figure: (a) Schematic representation of a cubic Mo4 S4 clusters. (b) A model of the three-dimensional aggregate reported in previous studies. (c) Schematic representation of superatomic layer "Mo 8 S8 Cl 11 ". <001>, <120>, and <100> represent the arrangement of the Mo 8 sadist 8 Cl 11 when viewed from different directions, respectively.
Figure: (a) Schematic representation of a cubic Mo4 S4 clusters. (b) A model of the three-dimensional aggregate reported in previous studies. (c) Schematic representation of superatomic layer "Mo 8 S8 Cl 11 ". <001>, <120>, and <100> represent the arrangement of the Mo 8 sadist 8 Cl 11 when viewed from different directions, respectively.
【Glossary】
*1: Cluster
A nanostructure consisting of multiple atoms aggregated by interaction. A typical example of a cluster is the C60 fullerene, a spherical molecule consisting of 60 carbon atoms.
*2: Superatom
A cluster whose properties vary with the type and composition of its constituent atoms and has discrete electronic states similar to those of atoms. Transition metal chalcogenide superatom have a highly symmetric structure, with M3X4 and M4X4, M6X8 (M: transition metal, X: chalcogen) and others have been reported.
*3:Nanoribbon
A one-dimensional material in the form of a strip (ribbon) of two-dimensional material cut into a thin width of nanometer size.
Click here to see the press release.【Japanese only】
Journal:Advanced Materials
Researcher's Information: Yasufumi Takahashi







 PAGE TOP
PAGE TOP